Jordan Facts and Figures
In the scale of nations, Jordan is an average, mid-sized country. In terms of population, its 6.5 million people rank 103rdI (about the same as Libya or Paraguay) out of 224 states and autonomous territories.

In the scale of nations, Jordan is an average, mid-sized country. In terms of population, its 6.5 million people rank 103rdI – about the same as Libya or Paraguay – out of 224 states and autonomous territories. Its area, comprising 89,342 km2 (34,495 mi2), is ranked 111th—slightly smaller than Portugal but a little larger than Austria.
Surrounded by Israel and the Palestinian West Bank along its western border, Syria to the north, Iraq to the northwest, and Saudi Arabia on eastern and southern borders, Jordan is located at the very center of the Middle East.
Geographically, Jordan is divided into three main areas: the Jordan Valley, the Mountain Heights, and the eastern desert, or Badia region.
Jordan Valley. The Jordan Valley, which is the country’s most distinctive natural landscape, is part of the Great Rift Valley, which extends south from Turkey through Lebanon and Syria to where it forms the Sea of Galilee, and continuing south until it enters Jordan at the point where the borders of Jordan, Syria, and Israel meet.
From this point, the east bank of the Jordan River forms the western boundary of Jordan with Israel and the Palestinian West Bank continuing all the way to where the river empties into the Dead Sea.
This area, which includes Jordan’s part of what was once called the “Fertile Crescent” is several degrees warmer than the rest of the country, but receives significantly more rainfall giving it lush vegetation and a year-round agricultural climate. The Jordan Valley is relatively narrow, with a width of sometimes less than 25km, and constitutes about 5% of Jordan’s land area.
Highlands.
Immediately to the east of the Jordan Valley rises the mountainous edge of the Great Rift known as the Jordan Highlands, which runs between the Jordan Valley and the Badia region or eastern desert plateau.
This region begins as steep mountains just to the east of the Jordan River reducing to rolling foothills farther to the east as it reaches the Badia region.
This region receives Jordan’s highest rainfall (c. 300 mm/yr); is the most richly vegetated region of the country; and contains most of Jordan’s cities, including Amman, Zarqa, Irbid and Karak.
Many peoples of the ancient world also found this region inviting, as indicated by the ruins of Jerash, Karak, Madaba, Petra, and many other historical sites testify. This region constitutes approximately 20% of Jordan’s land area.
Desert Plateau.
The Badia Region comprises the eastern 75% of Jordan’s land area, consisting of a desert or desert/steppe plateau about 1000 meters above sea level.
It is part of the North Arab Desert stretching into Syria, Iraq, and Saudi Arabia. Rainfall averages less than 50 mm. annually, resulting in little vegetation and few inhabitants or settlements.
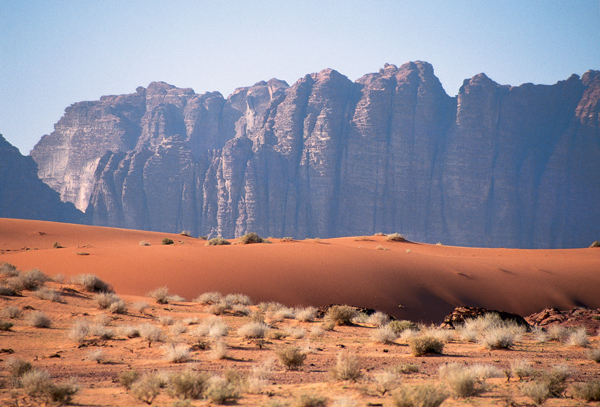
South of the Dead Sea and Amman the Great Rift mountains meld into the desert plateau to form the Rum Desert, home of the famous Wadi Rum, dominated by towering sandstone mesas producing some of the most fantastic desert-scapes in the world.